How to Use Optional Chaining in JavaScript
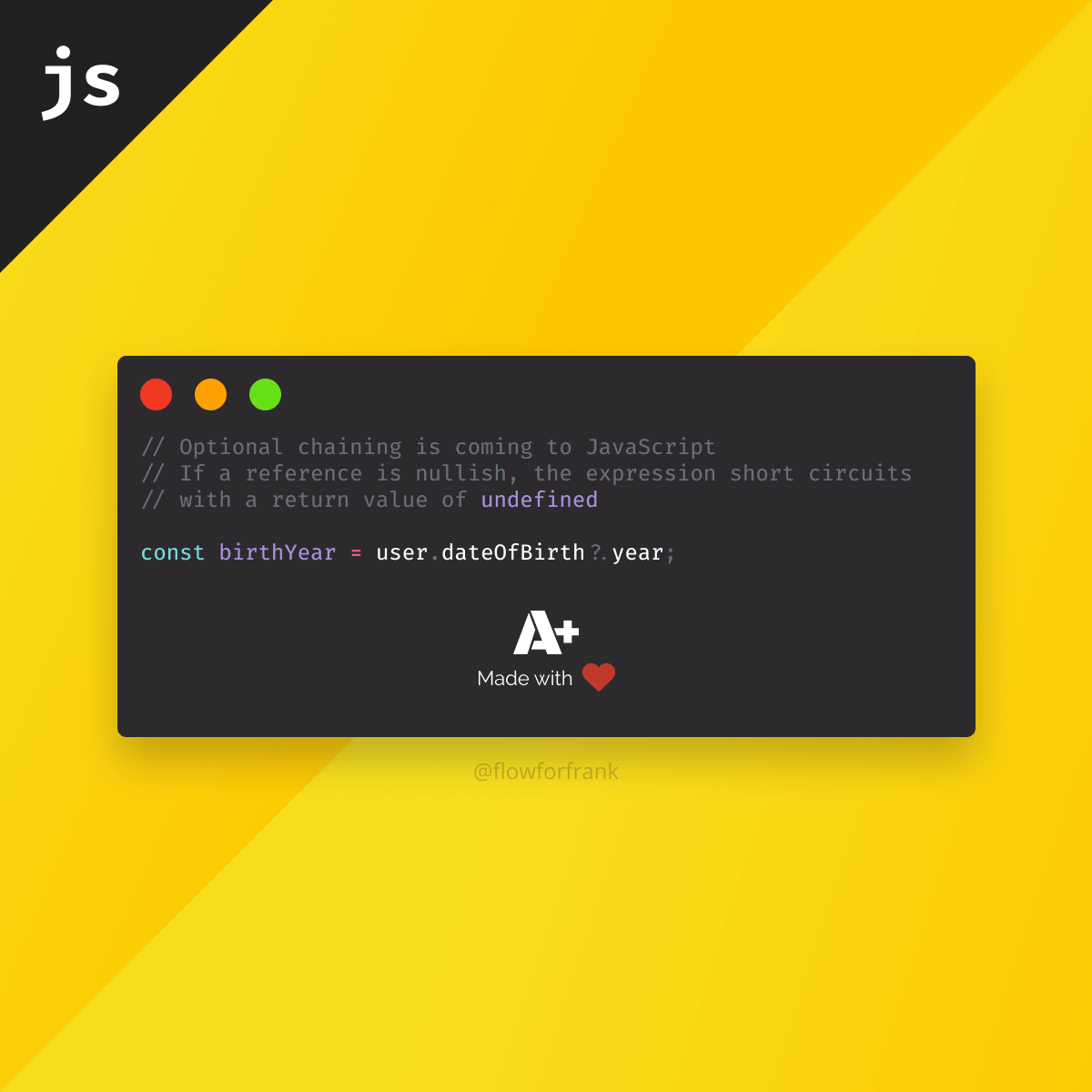
Optional chaining is coming to JavaScript. It lets you access deeply nested properties without having to explicitly check each object for its existence.
Instead of getting the famous “cannot read property of undefined” error message, the expression short circuits with undefined.
To use it, simply mark optional properties with a question mark:
// If `dateOfBirth` is undefined, `birthYear` will be undefined as well
const birthYear = user.dateOfBirth?.year;For full browser support, make sure you check the compatibility table on MDN.
Do You Need a Fallback Option?
If you rather want to use a more compatible version, you can achieve the same thing using a reduce function.
const getProperty = (obj, path) => (path.split('.').reduce((value, el) => value[el], obj));
const user = {
settings: {
theme: 'default'
}
};
getProperty(user, 'settings.theme'); // This will return “default”
getProperty(user, 'settings.invalidPath'); // This will return `undefined`
Resource

Rocket Launch Your Career
Speed up your learning progress with our mentorship program. Join as a mentee to unlock the full potential of Webtips and get a personalized learning experience by experts to master the following frontend technologies: