How to Use Schema Markup in HTML
This lesson is a preview from our interactive course
Schema markups are special HTML tags used to provide structured data to search engines. Defining schema markups can help your pages appear as rich snippets in search results.
These markups can take on various forms depending on the content of the page. In this lesson, we'll explore two common markups that are commonly used for content-based websites.
Website Schema#
Schema markups are defined inside script tags with a type of application/ld+json. To add details about a website using a schema, we can use a website schema markup:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "WebSite",
"url": "https://example.com",
"name": "Title of the website",
"description": "A short description about the website"
}
</script>Schema markups are JSON objects with special attributes. Each markup is defined by its @type attribute. To create a website schema, you can use the code provided above.
The @context and @type attributes are always required. The correct structure is defined by Schema.org. To validate a schema, you can use the Schema validator, which accepts either a URL to test or a code snippet.
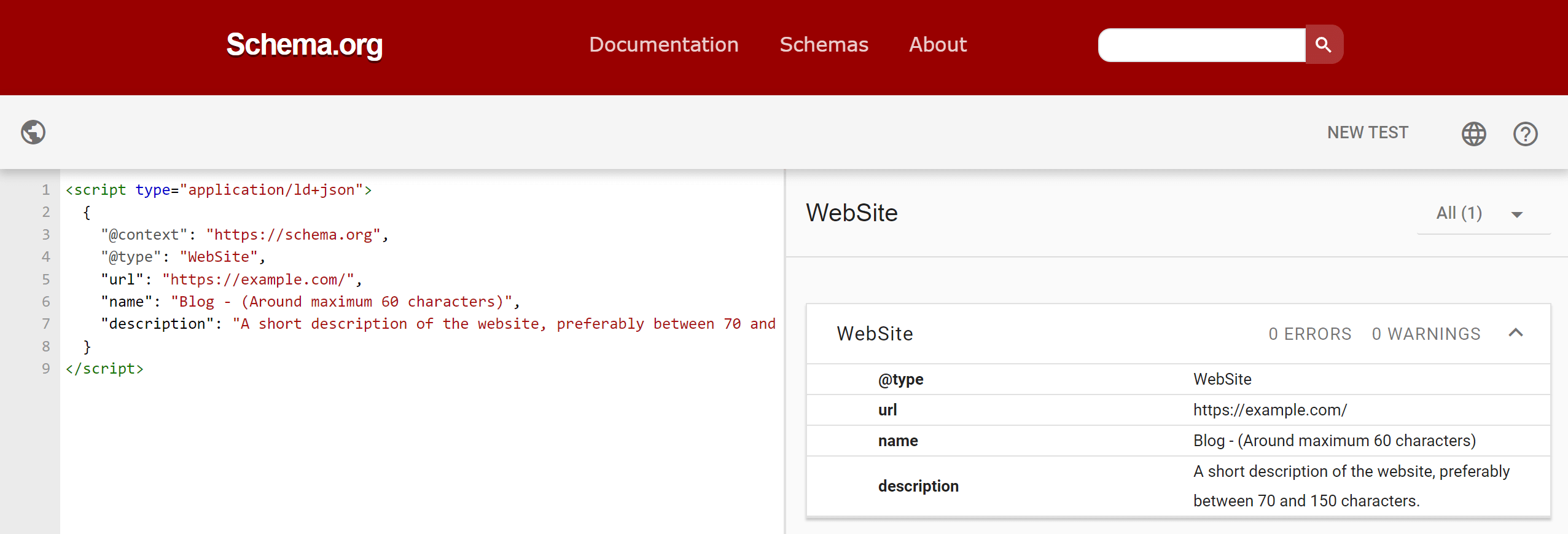
Invalid schemas may be ignored by Google, so it's always recommended to validate your syntax.
Article Schema#
Another commonly used schema markup is the article schema. This provides valuable information to Google about each article on a website. An article schema can have various attributes, but the most important ones are:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"url": "https://example.com",
"headline": "Title of the article",
"image": "/path/to/featured/image.png",
"description": "A short description about the article",
"dateCreated": "2023-08-16",
"datePublished": "2023-08-16",
"dateModified": "2023-08-24",
"keywords": ["Frontend", "HTML"]
}
</script>This time, the @type of the schema is "Article". Instead of using name, we can use the headline field to define the title of the article, and optionally, we can use the image property to define a featured image associated with the article.
Articles will also have a dateCreated, datePublished, and dateModified fields. These fields provide details on the freshness of the content. After publishing an article, only the dateModified should be updated.
Additionally, we also have a keywords field, which is a comma-separated list defining a set of topics for the article.
Reinforce your knowledge! What do we mean by semantic HTML?
Adding Authors#
We can further enhance the article schema to include information about the author of the article by creating a new object called author under the keywords node with the following three properties:
- A
@typeproperty with a value of "Person" - A
nameproperty with the name of the author - A
urlproperty pointing to either a contact page or a dedicated author page
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Down",
"url": "/authors/john"
}Adding Publishers#
Similarly, we can also do the same for the site to mark it as the original publisher of the article. Under the author node, we can create a new object called publisher with the following three values:
- A
@typeproperty with a value of "Organization" - A
nameproperty with the title of the page - A
urlproperty pointing to the home page
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Title of the page",
"url": "https://example.com"
}
Summary#
Schema markup comes in various shapes and forms. You can not only define schemas for websites, articles, authors, and organizations, but you can also define schemas for events, places, products, reviews, books, movies, and more than 800 other types.
For the full list of schemas and their available properties, you can refer to Schema.org. Defining proper types on your pages is essential if you want your pages to have a chance to appear as rich snippets.

Rocket Launch Your Career
Speed up your learning progress with our mentorship program. Join as a mentee to unlock the full potential of Webtips and get a personalized learning experience by experts to master the following frontend technologies: